One of the most common complaints that doctors hear from patients is knee pain. What causes this pain is not always possible to say right away. Knees can be affected by various diseases, for example, osteoarthritis of the knee joint. Also known as gonarthrosis.
Gonarthrosis is a non-inflammatory damage to the joints that often leads to cartilage destruction, bone deformity and limited movement. This disease has the code M17 in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10).
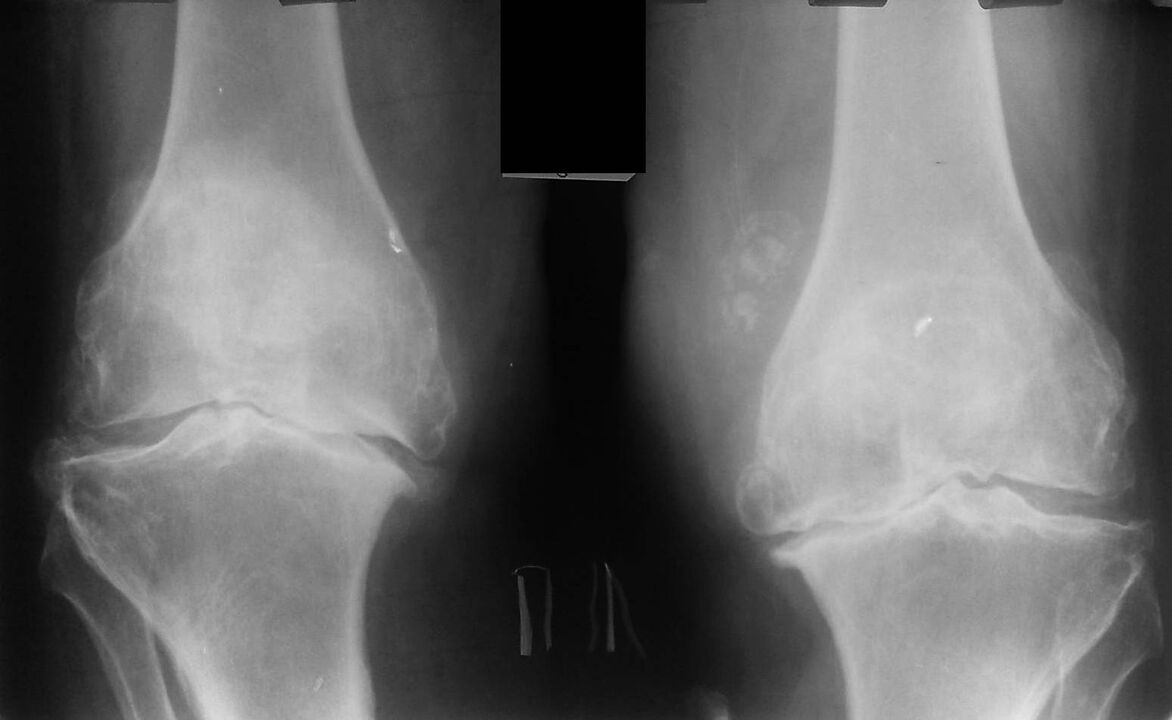
All patients can be divided into two groups. The first group includes young people, most often young people, with damage to one, less often to both knee joints. They have a knee injury or surgery in their medical history.
The second group includes obese, middle-aged or elderly people, most often women, in whom gonarthrosis has developed in several parts of the body simultaneously.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee
The symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee gradually increase. Patients may not be aware that they have been ill for years until they notice a noticeable deformity of the knee or severe pain.
At the same time, arthritis of the knee joint in the initial stage of the disease is more often accompanied by uncomfortable and painful sensations in the knees, and few people seek medical advice.
Women prone to obesity, especially after 40 years, are predisposed to this disease.
Varicose veins also contribute to the development of the disease. At this stage, it is possible to treat the disease at home without the use of tablets and ointments.
The pain is not sudden, it appears gradually, over several years. They usually occur during sports, walking and other physical activities.
Acute pain may not be a symptom of gonarthrosis, but the result of a rupture, meniscus damage, or bruising. It is the strong pain that becomes the motivation to turn to the specialist.
The pain often worsens in the following cases:
- when you walk;
- in a long standing position;
- along the slopes;
- when lifting the body from a sitting position;
- when carrying heavy items.
While performing these operations, the maximum load acts on the joint, therefore, if the patient feels severe discomfort, he can already be diagnosed with stage II knee joint arthritis. A person tries to move less, take a static position to avoid pain, but with constant physical activity, the anxiety returns.
Deforming osteoarthritis of the knee joint accompanies a symptom such as deformity. It becomes apparent already in the second or third stage of the disease. Her first signs: the knee was slightly swollen but retained its shape. In later stages, there is a change in the shape of the knee, making one leg shorter or longer.
One of the most characteristic symptoms is a crack in the key, visible in the second and third stage. The main thing is to distinguish the crackling sound in the joints of a healthy person from the dull and dry crackling of the patient. This sound causes weakening of the ligament apparatus or high mobility of the joints.
To ensure the immobility of the knee joint, it is recommended to wear knee braces.
Forms of gonarthrosis
There are two forms of the disease:
- Primary: Occurs as a result of abnormal congenital joint development.
- Secondary: Occurs as a result of illness and injury.
The main form of osteoarthritis of the knee joint often develops in childhood and is caused by improper formation of ligaments and joints. They are subjected to heavy loads and deform during physical activity.
The secondary form of the disease is caused by the following factors:
- Injuries (bruising, sprains, dislocations, fractures), which lead to violations of the structure of bones, ligaments and cartilage. All of this is a post-traumatic form of the disease.
- Operations when the meniscus is displaced violate the integrity of the knee structure.
- Lots of walking load (typical for weightlifters).
- Obesity. Excess weight provokes pressure on the cartilage of the knee joints.
- Passive lifestyle.
- Diabetes.
- Mosha.
- Arthritis (inflammatory process in the joints). Prolonged illness is associated with the formation of excess fluid in the joint cavity and causes complications.
- Metabolic disorders lead to the deposition of salts.
- knee transplant.
- Diseases that cause prolonged leg muscle cramps or vasospasm.
The development of the disease can take a unilateral or bilateral form. Trauma often causes gonarthrosis of the left or right side, and obesity is bilateral.
Stages of the disease
There are three stages of gonarthrosis:
- From the beginning of the first stage to the obvious manifestations of the disease, it can take months or even years. The person complains of persistent leg pain, especially when getting up or down stairs and getting out of bed in the morning. The photos usually show a narrowing of the connection between the joints and as a rule, instead of going to the doctor, patients use traditional medicine - ointments and tinctures.
- The second stage is characterized by more acute pain, which does not stop with the immobility of the limbs. A crack appears. Fluid accumulates in the ankle cavity, radiography shows deformation and growth of bone. The patient at this stage tries in every possible way not to move the affected limb. The attending physician prescribes injections and chondroprotectors - medicines that help restore cartilage tissue.
- In the last third stage, the pain becomes constant and often worsens with changing weather conditions. X-rays show a significant deformity of the knee, which can be corrected only with surgery, the patient must receive a complex of chondroprotectors. The patient's gait changes: he walks with legs half bent or rotates from side to side.
Causes of the disease. Groups at risk
Overweight
Most often, deforming osteoarthritis affects the elderly. A special group of risk includes overweight women after 40 years. The probability of pathology in obese people is 4 times higher than in people with normal body weight. The model is simple: the greater a person's weight, the faster the disease develops and the more severe it is. In this case, the form of the disease can be called acquired. It is the joints of the lower limbs that fall under impact because they are bound to carry the greatest load.
Overweight people also face hormonal imbalance and metabolic disorders, which contribute to the development of obesity and osteoarthritis.
Age
Elderly can be called those who have reached the age of over 60-65 years. In this population, osteoarthritis occurs in 65-85 percent of people.
The reason is age-related changes that negatively affect the structure of the joints. Even ordinary walking can become a considerable burden and stimulate the development of the disease, while the consumed cartilage can no longer heal on its own.
Congenital pathologies and hereditary factors
The disease can affect both young people and those who do not suffer from overweight. As a rule, in such situations, the disease occurs due to congenital defects of the knee joints, for example, lack of intra-articular lubrication. Inheritance also plays an important role.
However, most patients suffering from knee pain are people of respectable age. Osteoarthritis is rare in young people. Unfortunately, young patients do not always receive the treatment they need because not all physicians find it necessary to give them the attention they need.
High loads
People who earn a living by hard physical work and athletes of various levels are also at risk of experiencing osteoarthritis of the knees. In this case, the disease becomes an occupational pathology.
Operations, injuries and other diseases
Surgery, trauma, various joint diseases can provoke the appearance of gonarthrosis.

When the cause remains unknown, osteoarthritis of the knee joint is commonly called idiopathic.
Diagnosis of osteoarthritis of the knee joint
This diagnosis is made on the basis of patient complaints, examination data, palpation of the diseased ankle, and X-ray examination.
X-ray is a standard research method that allows you to confirm the diagnosis, determine the degree of pathological changes, monitor the dynamics of the process and also allows you to exclude other pathological processes (for example, tumors) in the tibia and femur. .
It should be noted that primary changes in knee joint structures on radiography may be absent. Next, the narrowing of the joint space and the compression of the subchondral area are determined. The articular ends of the femur and especially the tibia widen, the ends of the condyle become sharp.
Auxiliary methods of diagnosis are CT (computed tomography) and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), which allow a more detailed study of pathological changes in bone structures and the identification of changes in soft tissues.
How to treat knee joint gonarthrosis
The more acute the stage of the disease, the more complex the treatment of gonarthrosis becomes. The chronic nature of the pathology may remain in the remission phase, when the active manifestations of the disease are minimized or absent altogether.
Physiotherapy treatment in combination with chondroprotective drugs gives positive results.
Treatment options include:
- drug therapy (chondroprotectors);
- Surgical intervention;
- rehabilitation course (exercise therapy, massage, etc. ).
Drug treatment
With drug therapy, the use of non-steroidal analgesics is prescribed. These medications help relieve the pain and symptoms of synovitis (inflammation). If the pain is particularly strong or the synovium of the knee joint is very inflamed, then corticosteroids may be used. These drugs have a more potent analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect than non-hormonal sedatives. Muscle relaxants and antispasmodics will help periarticular muscles get rid of spasms.
Antioxidants and vasodilators improve cartilage nutrition. The main drugs for the conservative treatment of the disease are chondroprotectors containing chondroitin and glucosamine sulfate (natural components of cartilage).
The use of pathogenetic drugs should be systematic and prolonged.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy treatment methods (UHF, ultrasound or phototherapy) are considered as additional tools to speed up the healing process.
They also include:
- Acupuncture. This method relieves muscle spasm near the affected joint, normalizes metabolic processes in them, thus restoring damaged cartilage tissue.
- Hirudotherapy. Treatment with caterpillars has the same effect as injections, as it improves blood circulation.
- laser therapy. Such procedures relieve inflammation, swelling, improve metabolism and neutralize pain.
- Cryotherapy. Both treatments with liquid nitrogen and ordinary ice at home are effective.
- Magnetotherapy. The impact of the magnetic field not only improves blood circulation to the tissues, but also relieves swelling and inflammation.
- Electromostimulation. With the help of microcircuits of current of different frequencies, the muscles are restored and strengthened, and the blood circulation in the limbs is improved.
Treatment of knee gonarthrosis with physiotherapy is effective, as it reduces pain. The attending physician usually prescribes such treatment according to the stage of the disease.
Physiotherapy
Exercise therapy for osteoarthritis of the knee joint is one of the main tools for restoring atrophied muscle and should be performed very carefully and slowly. If the patient feels that the pain is returning, exercise should be discontinued.
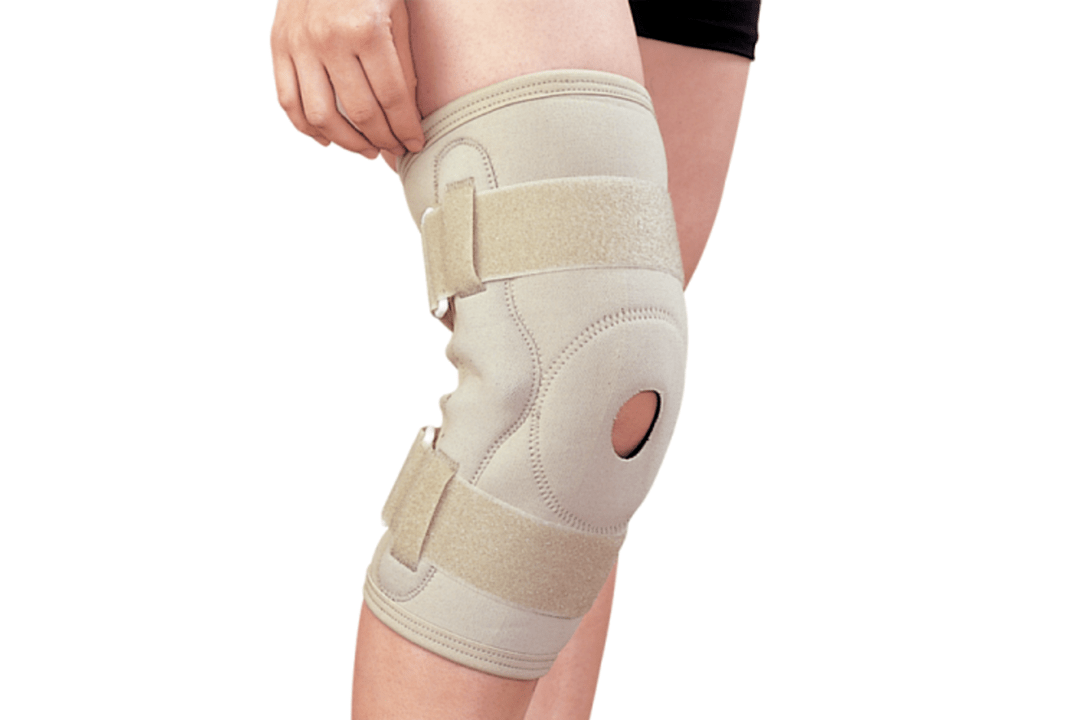
During therapeutic exercises, it is necessary to wear special knee-fixing pads. The rehabilitation course also includes the use of these orthopedic devices, their purpose is to reduce the load from the affected knee to the cane or prosthesis. Patients with gonarthrosis are often advised to wear knee braces to relieve pain while walking.
Therapeutic gymnastics for gonarthrosis reduces the load on the damaged joint, developing the leg muscles. Exercises that load the joint are strictly contraindicated. Water gymnastics and swimming are ideal activities.
Orthopedic Therapy
To reduce the load on the affected joints, the patient should use a cane. A good helper for knee osteoarthritis are orthopedic shoes that provide a natural foot position and even load distribution.
Massage
Massage relieves muscle spasms, reducing pain and increasing range of motion. This procedure also improves blood circulation and provides the joint with nutrients.
Surgical intervention
A marked decrease in work capacity (especially up to 45 years) requires surgical treatment. The choice between corrective methods (osteophyte removal) and radical (knee arthroplasty) treatment depends on the stage of the disease, the patient's age, symptoms and other factors.
Nutrition
As for the special diet for gonarthrosis, it most often aims to reduce the patient's weight because it is overweight that leads to joint overload. It is recommended to eat small meals every 3 hours, eat lean meat (chicken, turkey, rabbit) and exclude fatty pork and get the necessary proteins from legumes.
Refined oil should be replaced with unrefined oil, salt intake should be limited. Therapeutic diet also means rejecting canned foods, fried and smoked foods. To restore damaged cartilage, it is necessary to provide the body with carbohydrates, which are found in cereals and cereal flour.
In addition, it is recommended to drink freshly squeezed juices, such as carrots, beets and apples, to remove toxins and reduce inflammation in the body.
Various fish and jellies act as chondroprotectors and help restore cartilage not only in the initial stages but also during periods of irritation.
Popular methods of treatment
There are many ointments, compresses, tinctures used by lovers of traditional medicine. These medicines are usually made from herbs, medicinal bile and help improve circulation in the joints.
Compresses and ointments also relax the muscles, their effectiveness is very high, but in the third stage of gonarthrosis without the use of medication, they are practically useless.
Traditional medicine should not be neglected because they help relieve anxiety and greatly reduce the symptoms of the disease. But in any case, you should consult a doctor and not do self-medication.
There are contraindications, it is necessary to consult a specialist.
prevention
It is recommended to adhere to the following principles of a healthy lifestyle:
- Balanced diet;
- giving up bad habits (smoking, alcohol);
- sports;
- maintaining a healthy weight;
- prevention of sports injuries (bruising, dislocation, fractures).
Knee osteoarthritis has several treatment options depending on the age and physical condition of the patient. To prevent and control the disease in the early stages, sports as well as timely treatment are needed.



















